One To One Mapping Using Annotation
This will also help you to get overall idea of Hibernate one-to-one mapping with detailed example.
When one class entity is mapped to another class entity is called as one to one mapping
In one-to-one mapping, the user and address entity are directly connected to each other. For example, in any application, a single user can have a single address, or a single address can belong to a single user.
The fetching of user records will also fetch address records from the database. Similarly, the fetching of user records will also fetch address records from the database.
This will give you an overall idea on how one-to-one hibernate xml works. It will also help you to answer most of the practical interview questions.
As part of this discussion, we will be creating sample Hibernate program to select, insert and delete data in MySQL database.
Pre requisite before starting hibernate development is to have Java, MySQL and Eclipse installed in local.
Below Example will help to create Hibernate project using Eclipse to insert data in MySQL database.
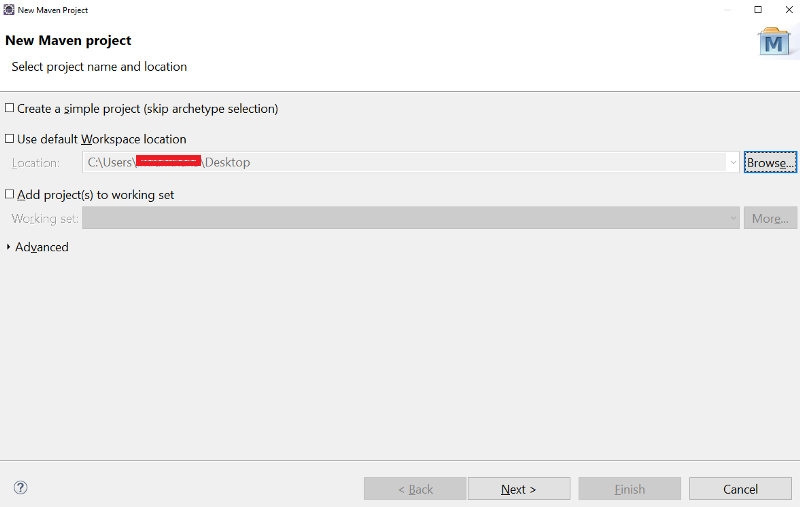
- Let’s create a maven project using Eclipse.
Click on File in top navigation and select New and than click on maven Project.
File → New → Maven Project
Below window will appear, no changes are required and click on Next
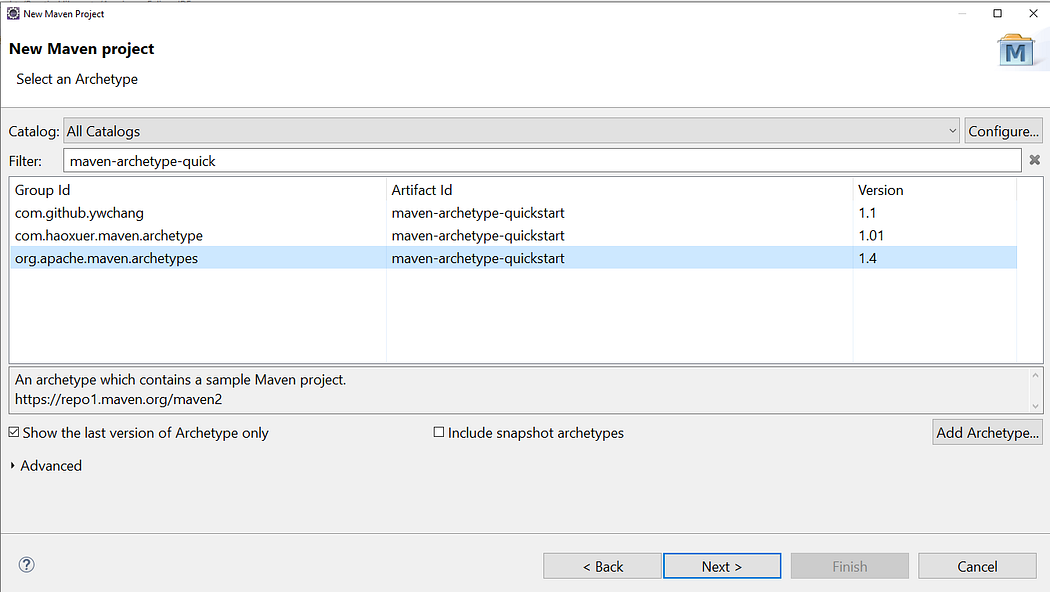
2. Wait for sometime or archetype to get appear on screen. Select below highlighted archetype Artifact Id as maven-archetype.quickstart and Group Id as org.apache.maven.archetypes.
click on Next after below inline selection.
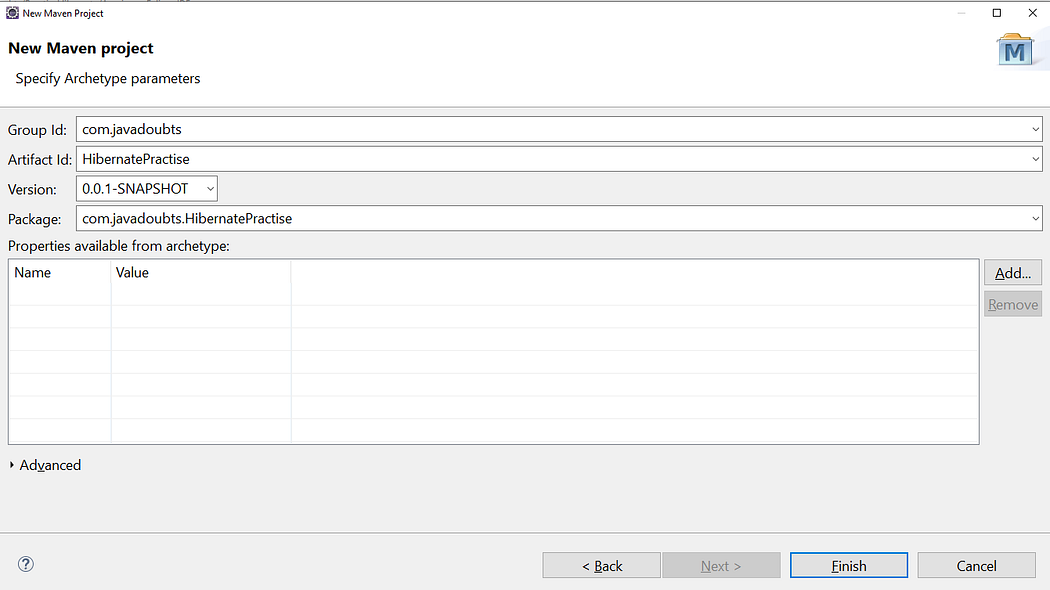
3. provide the Group Id and Artifact Id as mentioned below. Click on Next.
4. Copy paste below dependencies for hibernate and mysql under dependencies section in pom.xml.

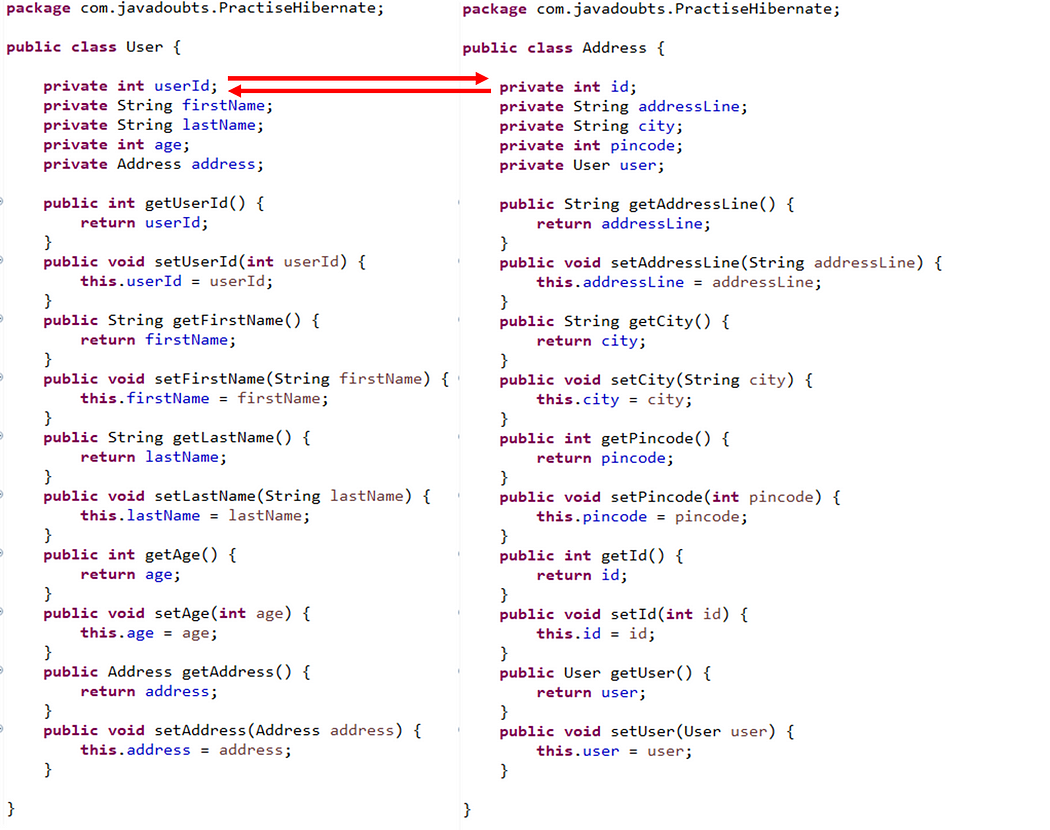
5. Create a User.java and Address.java inside com.javadoubts.PractiseHibernate package which will be persistence object to save data in database.
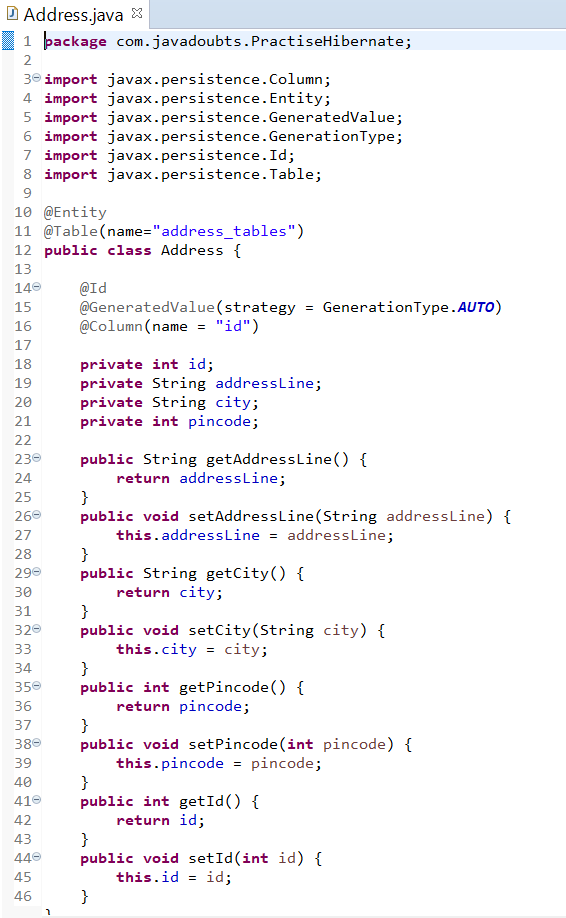
To create one-to-one mapping, it is required to create Address variable in User.java class and User variable in Address.java class.

6. Create resource folder under below highlighted hierarchy.
Very important Step:
right click select Build Path option and than select Use as Source Folder.

7. Create User.java file to provide mapping of User class and MySQL user_table table.
Create mapping for class variables and table columns.
It will also require to create a mapping of User.java class with Address.java as highlighted below red in color.
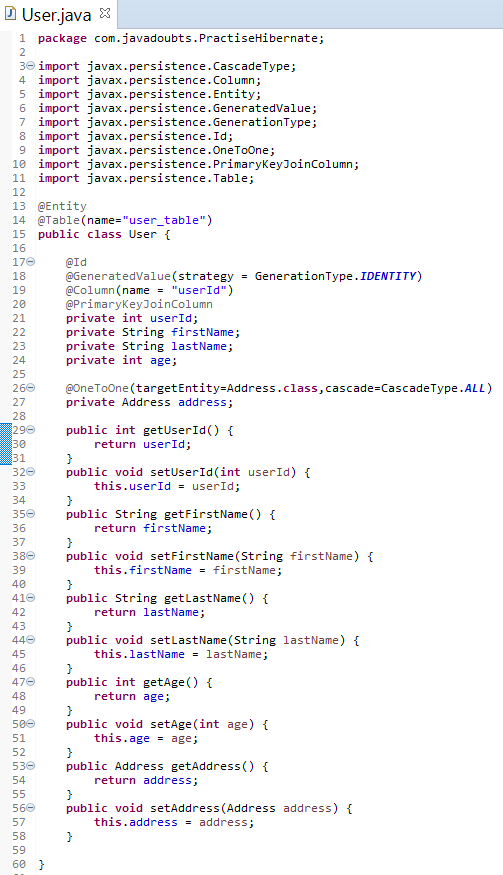
@Entity is to convert bean in to an entity.
@Table annotation helps us to map current bean as table. name attribute help us to map bean class name with MySQL table name. name attribute is not required if class name and table name is same.
@Column annotation helps to map class variable and MySQL column name.
@id represents to unique ID attribute in class map to the primary key of the database table.
@GenerateValue helps to generate unique id for given column.
@PrimaryKeyJoin column is very important as it helps us to create mapping between id’s.
8. Create Address.java file to provide mapping of Address class and address_tables MySQL table.
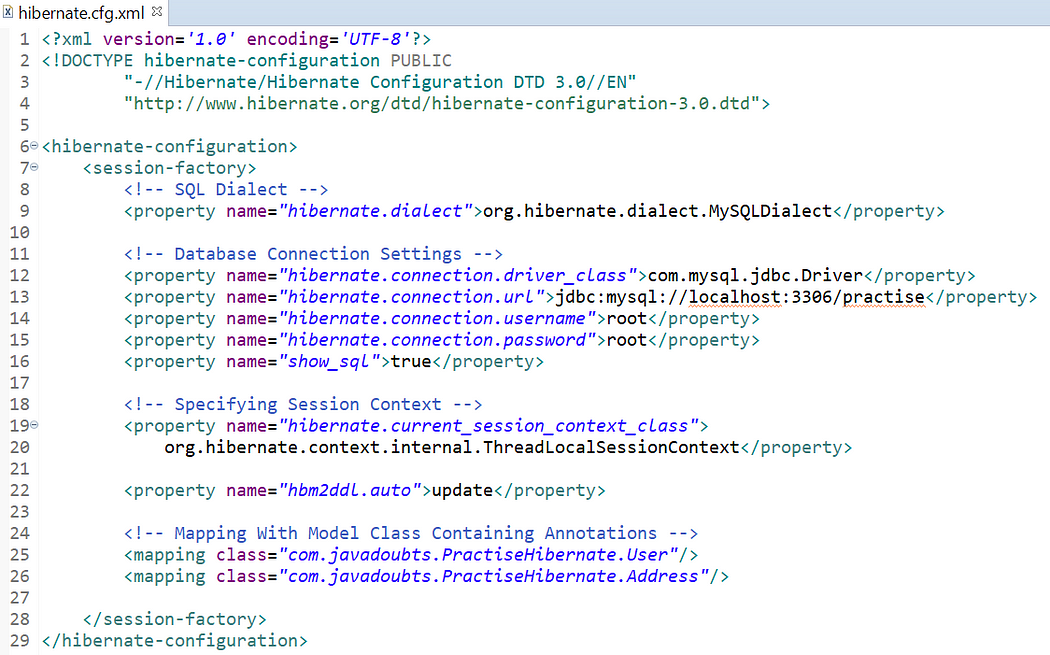
9. Create hiernate.cfg.xml file to provide info related to database connection as mentioned below.
10. Copy paste below code to App.java class. This class will help to load Hibernate bean class with annotations.
In below code, we have saved user data with the help of bean class without using SQL query.

12 Go hibernate.cfg.xml and update below line to create and run program to create table.
<property name=”hbm2ddl.auto”>update</property>
Please go back to MySQL and check if both the tables got created in MySQL with name address_tables and user_table.
If table didn’t get create, please run below script in MySQL editor or command prompt.
create table user_table(userId int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, firstName varchar(20), lastName varchar(20), age int, primary key(userid));
create table address_tables(id int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, addressline varchar(20), city varchar(20), pincode int);
If table get create in MySQL, please change it to update as mentioned below:
<property name=”hbm2ddl.auto”>update</property>
Re-run the program again below print below output.
OUTPUT:


Imran Khan, Adobe Community Advisor, certified AEM developer and Java Geek, is an experienced AEM developer with over 12 years of expertise in designing and implementing robust web applications. He leverages Adobe Experience Manager, Analytics, and Target to create dynamic digital experiences. Imran possesses extensive expertise in J2EE, Sightly, Struts 2.0, Spring, Hibernate, JPA, React, HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript.
