Javadoubts

Python Data Structure
This is a complete guide to understanding Python data structure with methods and examples.
This post may be a little bit long. But, it will provide end-to-end complete knowledge of Python data structures, including similarities and differences.
Below are the four data structure defined by Python to store data.
List
languages = [“CSS”, “HTML”, “Java”]
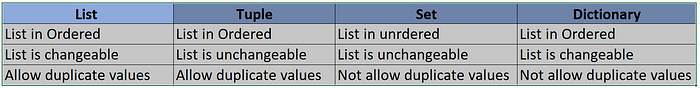
List is declare by using square bracket, it is ordered, allow duplicate values, changeable(allow update and delete items). The list uses square brackets to accommodate all items.
Tuple
languages = (“CSS”, “HTML”, “Java”)
Tuple is declare by using round bracket, it is ordered, allow duplicate values, unchangeable(update and delete items not allowed). The Tuple uses round brackets to accommodate all items.
Set
languages = {“CSS”, “HTML”, “Java”}
Set is defined by curly braces, it is unordered, duplicate values are not allowed, unchangeable(update and delete items not allowed). The Set uses curly braces to accommodate all items.
Dictionary
dictionaryOne = {
“name” : “test”,
“id” : “123”
}
Dictionary is ordered, duplicate items are not allowed, unchangeable(update and delete items not allowed). The dictionary in similar to JSON object.
Differences in between List, Tuple Set and Map

Imran Khan
Specialist Master (Architect) with a passion for cutting-edge technologies like AEM (Adobe Experience Manager) and a proven track record of delivering high-quality software solutions.
- Languages: Java, Python
- Frameworks: J2EE, Spring, Struts 2.0, Hibernate
- Web Technologies: React, HTML, CSS
- Analytics: Adobe Analytics
- Tools & Technologies: IntelliJ, JIRA
📝 Blogs
javadoubts.com © All rights reserved