Operators
Operators are used to perform some operations between operands.
a = 2
b = 3
print(a+b)OUTPUT:
5
Below are the different types of operators
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators

Assignment Operator:
Assignment operator are used to assign value to a variable. = (equal) symbol is use as an assignment operator.
In the below code value 3 is assigned to a with the assignment operator.
a = 3
Comparisons Operator:
It uses to compare two operands.

Logical Operator:
Logical operator also called as a Boolean operator as it returns true or false after comparison.
Logical operators are used to perform or compare more than two conditions. We have three types of bitwise operations:
- Logical and: It will return true, if all the operands are true.
print( 3 != 4 and 5 != 6)
OUTPUT:
True
2.Logical or: It will return true, if one of the operand are true.
print( 3 != 4 or 5 != 6)
3. Logical not: It will return true, if operand or operands collectively return false.
print( not 4 != 4)
OUTPUT:
True
Bitwise AND (&) Operator:
Bitwise operator can be easily understood by below table:

Example:
What will the output for bitwise operation of (5 & 9)

print( 5 & 9 )
Output: 1
Bitwise OR (|) Operator:
Bitwise operator can be easily understood by below table:

Example:
What will the output for bitwise operation of (5 | 9)

print( 5 | 9 )
Output: 13
Bitwise XOR (^) Operator:
Bitwise operator can be easily understood by below table:

Example:
What will the output for bitwise operation of (5 ^ 9)

print( 5 ^ 9 )
Output: 12
Bitwise Complement:
Bitwise operator can be easily understood by below table:
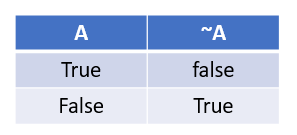
Example:
What will the output for bitwise operation of (~5)

print( ~ 5)
Output: -6
Note: Compiler gives 2’s complement of number. 2’s compliment of 10 is -6.
Identity Operators
It compare the equality and memory of objects. There are two types of identity operators
is operator
It will return true if the compare variable is referring to the same object

is not operator
It will return true if objects are not equal.

Membership Operator:
The membership operator is used to check if a particular value is present in the collection of values. It’s mainly used for str, list and tuples.
There are two types of operators:
in operator
It will return True if a particular value is present in the collection of values.
In below example the output is True as 2 as an integer not present in list.

not in operator
It will return True if a particular value is not present in the collection of values.
In below example the output is True as 2 as an integer not present in list.


Imran Khan, Adobe Community Advisor, certified AEM developer and Java Geek, is an experienced AEM developer with over 12 years of expertise in designing and implementing robust web applications. He leverages Adobe Experience Manager, Analytics, and Target to create dynamic digital experiences. Imran possesses extensive expertise in J2EE, Sightly, Struts 2.0, Spring, Hibernate, JPA, React, HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript.
